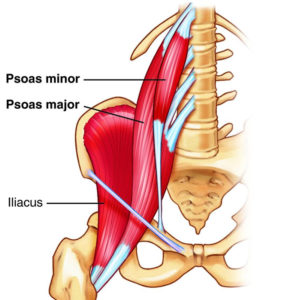
Most people have never heard of the psoas muscles, much less know where they are or how to pronounce the name (“SO-as”). Yet problems with these muscles often play a role in hip, groin, and low back pain. (see infographic at the bottom of the page. The psoas is a general term, but most often refers to the combination of two muscles, the iliacus and the psoas major muscle. Together these two muscles are better known as the Iliopsoas muscle.Each of these long, thick muscles originates deep in the abdominal cavity, from the sides of vertebrae in the lower half of the spine, and runs downward into the pelvis where it joins with another muscle (the iliacus) before attaching to the femur (thigh bone). Basically, the two psoas muscles connect the low back to the thighs, as shown in the illustration below.
These two muscles are important as hip flexors and low back stabilizers. The psoas minor helps to stabilize with its action of tilting the pelvis posteriorly and the major abducts, laterally rotates and flexes the hip along with the iliacus. Because of these attachments, a weak iliopsoas muscle could affect the position of the lumbar spine and produce a flat or sway back.
The Hip Flexors Associated Problems
As part of a group of muscles categorized as hip flexors, the psoas muscles’ primary action is to flex the hips in order to lift the thighs toward the torso, which allows you to run, walk uphill, and climb stairs, for example. They are vital for flexibility and movement of the back, pelvis, legs, and hips. And along with the core muscles, they help stabilize the spine.
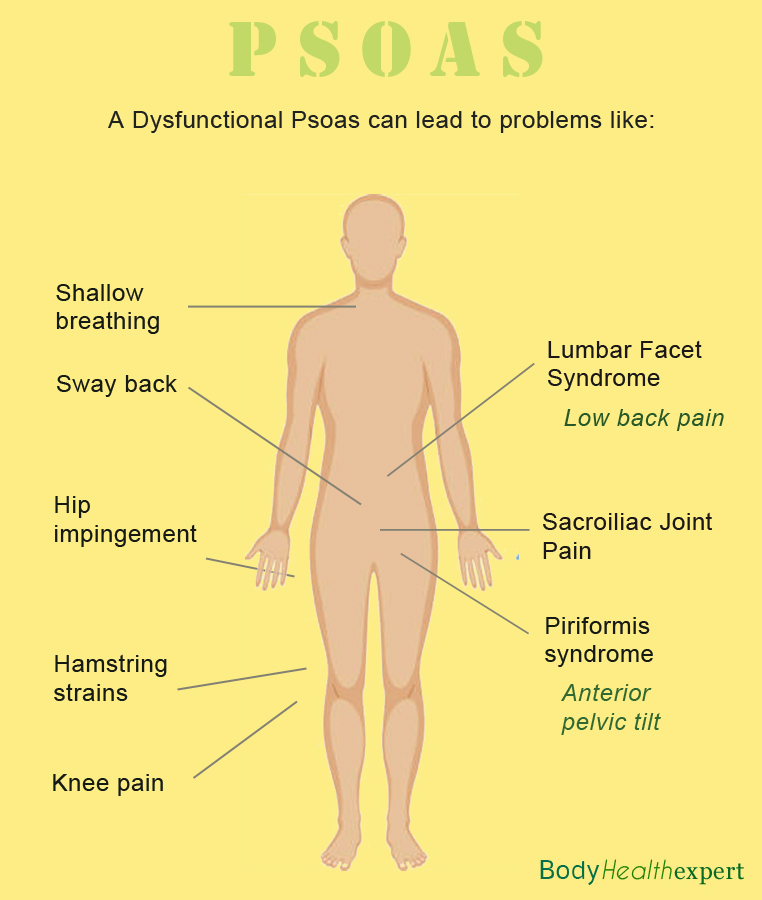
People commonly associate back pain with the psoas. The thought is often that the psoas is either too weak and not supporting the back which leads to pain or that the psoas is too tight creating a strong lordosis which is causing back pain.
Sitting for hours on end, such as at work or in a car, is probably the most common contributor to shortening of the psoas muscles.On the other hand, many athletes, including runners, soccer players, and cyclists, as well as dancers, end up with tight psoas muscles because they are prone to overuse them.
How to Train Your Psoas to Work Optimally
When the psoas muscle functions well, it has the power to
- help you achieve peak performance day after day after day.
- rapidly drop ugly body fat that stubbornly clings to your body.
- train harder, heavier and gain strength faster than you thought possible.
- hit your peak of sexual health.
- flood your mind and body with renewed energy and vigor.
Learn the Sequential Flow Method to release your hip flexors.